
What is blockchain? The short answer to that question is: the future of our digital lives. A blockchain is a distributed and immutable ledger (i.e. cannot be altered) that records transactions across a network of multiple computers. By distributing identical copies of the database across a network, blockchain technology eliminates the need for a central authority, thereby democratizing data and fostering an environment of trust and collaboration.
Blockchain’s design makes it highly secure and lends itself to a host of applications beyond its initial use in cryptocurrency systems like Bitcoin. The blockchain’s ability to ensure transparency and prevent fraud makes it an attractive tool for sectors like finance, healthcare, and supply chain management. Whether it’s facilitating cross-border payments, ensuring the provenance of goods in a supply chain, or enabling smart contracts to execute transactions, blockchain is transforming how we interact with the digital world.
Understanding blockchain is becoming increasingly important. It holds the potential to be a driving force in the future of secure and decentralized transaction systems across a range of industries. Blockchain’s distributed ledger technology enables secure, transparent, and tamper-proof transactions. This is crucial because it addresses a fundamental problem in digital transactions: the issue of trust.
By eliminating the need for a central authority or intermediary, blockchain technology democratically distributes control and verification amongst its network of users. This decentralization not only enhances security and privacy but also reduces costs and transaction times significantly. The implications of widespread blockchain adoption could lead to profound changes in how businesses operate and how everyday transactions are conducted. This in turn could open a new era of digital innovation and trustless interactions. This is why grasping the importance of blockchain is essential for anyone looking to understand the future landscape of technology and business.
There are several key features that make up blockchain technology:
1. Decentralization: Unlike traditional databases managed by a central authority (e.g., banks, governments), blockchain operates on a decentralized network of computers (nodes). This means no single entity has control over the entire network, enhancing the system’s resilience and security.
2. Transparency: Every participant with access to the blockchain can view the transactions stored in it. Depending on the blockchain’s nature (public or private), this transparency ensures that activities within the ledger are open and verifiable by all participants, fostering trust.
3. Immutability: Once a transaction is confirmed and added to the blockchain, it cannot be altered or deleted. This immutability ensures the integrity of the transaction history, making fraud and manipulation extremely difficult.
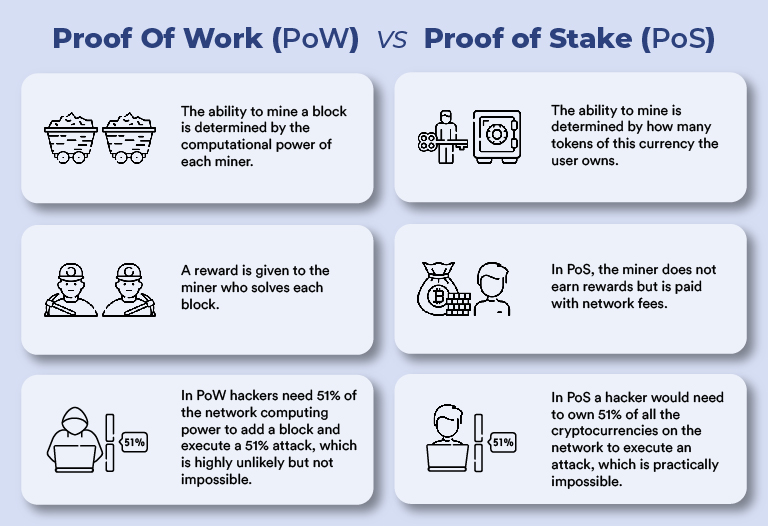
4. Consensus Mechanisms: Blockchain uses consensus models like Proof of Work (PoW) or Proof of Stake (PoS) to validate transactions and add new blocks to the chain. These mechanisms require agreement among network participants, ensuring that each transaction is verified and agreed upon before being permanently recorded.
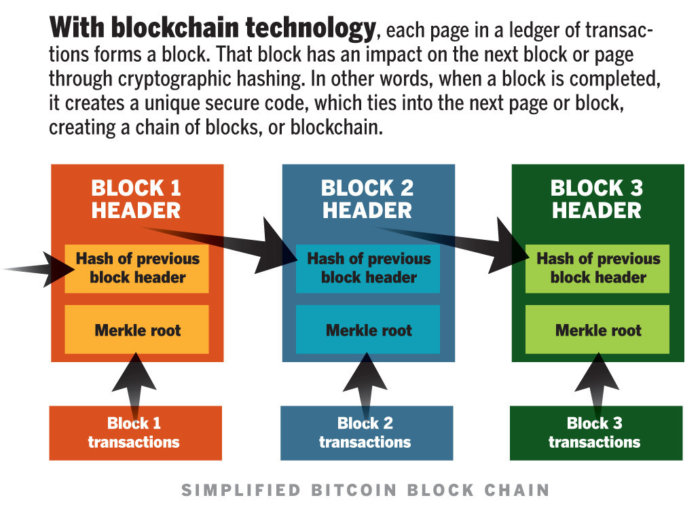
5. Security: Transactions on a blockchain are secured through cryptographic algorithms, making them tamper-proof. Each block is connected to the previous one through a cryptographic hash, forming a chain that enhances security as altering any part of the chain would require changing every subsequent block.
6. Smart Contracts: Some blockchains, like Ethereum, allow for the creation and execution of smart contracts—self-executing contracts with the terms of the agreement directly written into lines of code. These contracts automatically enforce and execute the terms of agreements without the need for intermediaries, streamlining various business processes.
7. Distributed Ledger: Blockchain is a type of distributed ledger technology (DLT), where each participant on the network has access to a shared ledger. This ledger records all transactions across the network, ensuring that data is consistent and accurate across all nodes.
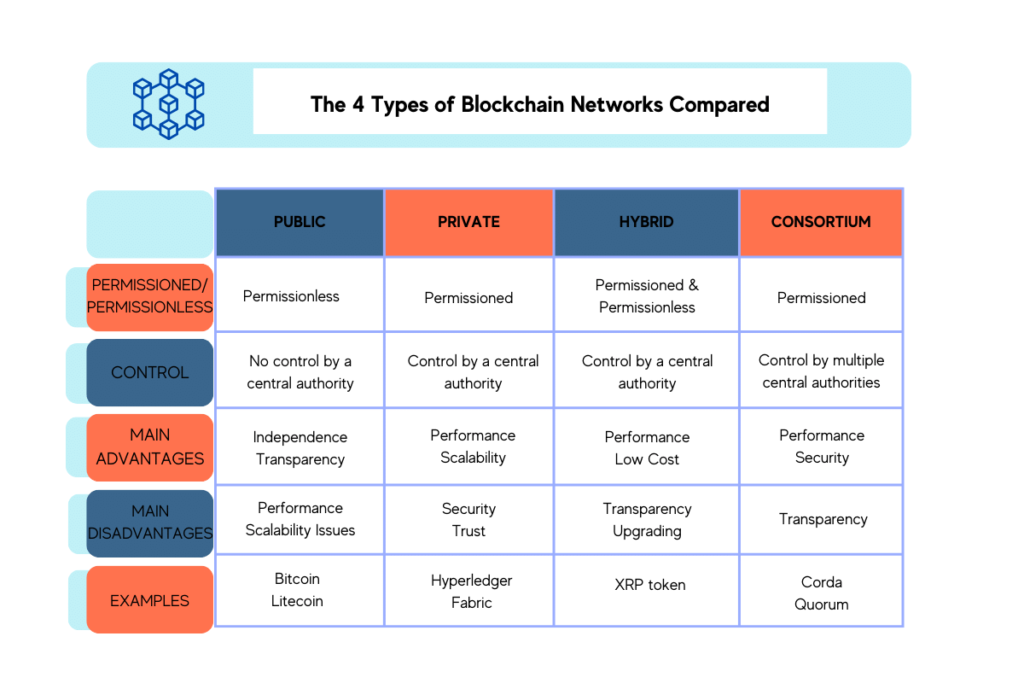
Public blockchains are fully decentralized and accessible to anyone interested in joining the network. This openness is a defining characteristic of cryptocurrencies like Bitcoin and Ethereum. Public blockchains employ various consensus mechanisms like Proof of Work or Proof of Stake to ensure that all transactions are validated and that the network remains secure and resistant to fraud. The transparent and immutable nature of public blockchains makes them the ideal foundation for trustless transactions and the creation of distributed applications.
Private blockchain networks are permissioned, meaning that access is restricted to specific users. This exclusivity makes private blockchains a go-to choice for businesses and organizations that require privacy and more control over their blockchain operations. Not only do private blockchains maintain the inherent security features of blockchain technology, but they also offer improved scalability and faster transaction speeds due to the limited number of participants. Enterprises often leverage private blockchains for supply chain management, internal record-keeping, and to streamline various processes without exposing sensitive information to the public. The tailored access, control, and enhanced privacy of private blockchain networks underscore the adaptability of blockchain technology to fit the needs of diverse applications beyond the decentralized ethos of public blockchains.
Consortium blockchain networks represent a middle ground between the open nature of public blockchains and the restricted access characteristic of private blockchains. In a consortium blockchain, multiple organizations govern the network collaboratively. This type of blockchain is ideal for business scenarios where all participating entities need to have permission to access the blockchain and have a stake in the network’s success and security.
Key characteristics of consortium blockchains include:
Due to their ability to share data securely, while retaining some control over network operations, consortium blockchains are commonly used in industries like finance, healthcare, and supply chain management. The hybrid-like approach combines the best of both worlds, offering the benefits of blockchain technology with the necessary oversight and management that enterprises demand.
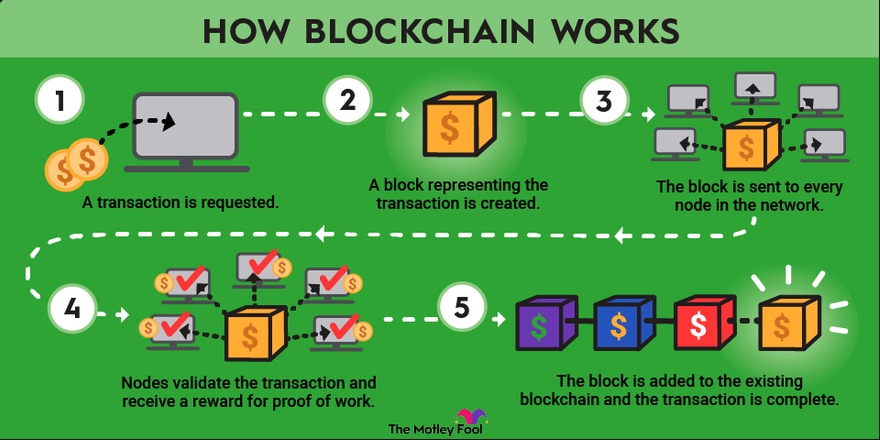
1. Record the Transaction
The first step is to record the transaction. When a transaction occurs, it is broadcast to a network of peer-to-peer computers, scattered across the globe, known as nodes. This decentralized network of nodes is tasked with validating the transaction through a process referred to as consensus.
2. Gain Consensus
A blockchain achieves consensus through a specific set of rules or mechanisms that allow all the participants (nodes) in the network to agree on the validity of transactions and the current state of the ledger. This process ensures that every copy of the distributed ledger is the same across all nodes, maintaining the integrity and security of the blockchain. There are several consensus mechanisms, but the two most common are:
3. Link the Blocks
Once the transaction is confirmed, it forms part of a new block, which is then cryptographically linked to the preceding block, forming a chain—hence the term “blockchain.” Every block contains a unique hash, a sort of digital fingerprint, as well as the hash of the previous block, and this sequential hashing is crucial for the security of the blockchain. It ensures that once a block is added to the ledger, altering it retroactively would require enormous computing power to change the entire chain. For one source to efficiently harness such computational power is virtually impossible, thus cementing blockchain’s role as a ledger impervious to fraud.
4. Share the Ledger
Now that the transaction has been recorded, verified and the blocks have been linked, the next step is to share the ledger. This means the blockchain ledger is distributed across a network of computers, often referred to as nodes. This distributed ledger technology (DLT) ensures that every participant in the network has access to an up-to-date copy of the ledger, creating unparalleled transparency. By sharing the ledger, blockchain enables a level of visibility that was previously unattainable in financial transactions and data exchange. This transparency ensures that all network participants can verify and audit transactions independently and in real-time.
Blockchain technology is most famously used as the foundation for cryptocurrencies, such as Bitcoin and Ethereum. These digital currencies leverage blocklchain’s decentralized nature, allowing for secure, transparent transactions without the need for a central authority, like a bank. This not only reduces transaction costs but also opens up financial services to parts of the world that are underserved by traditional banking institutions.
Smart contracts are self-executing contracts with the terms of the agreement directly written into lines of code. These contracts run on blockchain technology, ensuring that the contract automatically enforces the terms of the agreement as soon as the conditions are met. This application of blockchain can revolutionize various sectors by automating processes, reducing fraud, and removing the need for intermediaries in legal and business transactions.
In supply chain management, blockchain provides a transparent and unchangeable ledger, allowing all parties in the supply chain to track the production, shipment, and receipt of products in real time. This visibility helps reduce losses from counterfeit, improves regulatory compliance, and enables more efficient recalls of defective products, enhancing consumer trust and safety.
Blockchain has the potential to significantly improve the integrity and security of voting systems. By recording votes in a manner that is secure, anonymous, and impossible to alter after the fact, blockchain can reduce the risk of fraud and ensure that the electoral process is fair and verifiable, thereby increasing public trust in the electoral process.
In the retail sector, blockchain enables more secure and transparent transactions, loyalty programs, and supply chain visibility. Retailers can use blockchain to authenticate products, prevent fraud, and provide customers with a detailed history of the product journey, from production to sale. This can significantly enhance consumer trust and loyalty in a brand.
Blockchain technology is transforming the media and entertainment industry by enabling direct transactions between creators and consumers, effectively reducing piracy and ensuring that artists receive fair compensation for their work. Additionally, it can provide transparent royalty distribution, immutable content ownership records, and new models for content licensing, thus opening up new avenues for creators to monetize their work and engage with their audience. The benefits that blockchain can bring to creators is a prime example of how this technology expands commercial democracy.
The accuracy of the blockchain is maintained through its decentralized verification process. Each transaction added to a blockchain must be validated by multiple nodes (participants) in the network, ensuring that each entry is correct and tamper-proof. This process significantly reduces human error and the risk of fraud, leading to a highly accurate and reliable system for recording transactions and data.
Blockchain technology reduces costs for organizations by eliminating the need for middlemen or intermediaries in various processes, such as payments, real estate transactions, and even legal processes. By facilitating peer-to-peer transactions and automating contracts through smart contracts, businesses can significantly lower their operational costs and fees associated with traditional financial transactions and business agreements.
Blockchain enables more efficient transactions by allowing the transfer of assets directly between parties without the need for a central clearing authority. This process can significantly speed up transaction times, especially in cross-border trades, which typically take several days to clear through traditional banking systems. With blockchain, these transactions can be completed in minutes or even seconds, enhancing operational efficiency.
One of the most significant benefits of blockchain is the high level of security it provides. Once a transaction is recorded on a blockchain, it is encrypted and linked to the previous transaction, creating a chain of blocks that is nearly impossible to alter. This security feature helps prevent fraud and unauthorized tampering, making blockchain an ideal platform for recording sensitive transactions and data.
While blockchain is known for its transparency, it also offers solutions for maintaining privacy. Through mechanisms like zero-knowledge proofs, participants can verify transactions as valid without revealing any sensitive information about the parties involved or the transaction details. This feature enables users to enjoy the benefits of the blockchain while protecting their privacy.
Transparency is another core benefit of blockchain. Since every transaction is recorded on a distributed ledger and accessible to all network participants, blockchain provides an unprecedented level of openness and transparency. This visibility helps build trust among users, as they can verify transactions independently and ensure that the system operates fairly and without bias.
How does blockchain ensure data integrity and protect against fraud? At its core, blockchain is renowned for its robust security measures which are engineered to establish trust in a trustless environment. Each block within the chain is encrypted and linked to the previous one, creating an immutable ledger that is virtually impervious to tampering. Moreover, decentralization plays a pivotal role in safeguarding the network. With numerous nodes (or computers) verifying transactions and maintaining the ledger simultaneously, the system is protected against single points of failure – a vulnerability in most traditional centralized systems. These features combined with advanced cryptographic techniques make blockchain a powerhouse in maintaining data reliability and security. This security aspect is not just a promise; it’s an operational reality that has fueled the adoption of blockchain across industries far beyond its initial application in cryptocurrency.
As blockchain technology continues to grow and become more accessible, it is crucial to understand the principles behind it and how it can be leveraged for future innovations. By demystifying blockchain and highlighting its practical applications, this post hopes to provide clarity and insight into its transformative potential, essentially offering a glimpse into a future where blockchain technology is woven into the fabric of our daily digital interactions.
Reach out to us today and get a complimentary business review and consultation.