
Are you curious about the future of digital currency management? Web3 wallets are rapidly becoming the gateway to a decentralized financial landscape, offering innovative ways to store, manage, and interact with cryptocurrencies like never before. In this blog post, we’ll dive into the world of web3 wallets, exploring their revolutionary features and how they empower users with unprecedented security and control over their digital assets.
Understanding Web3 Wallets
What are Web3 Wallets?
Web3 wallets are digital wallets that allow users to store, send, and receive cryptocurrencies and interact with decentralized applications (dApps) on the blockchain. Unlike traditional wallets, they offer direct control over one’s digital assets without the need for intermediaries, such as banks or traditional financial institutions. Beyond crypto transactions, digital wallets also store digital assets like NFTs and identity data to facilitate digital verification.
How do Web3 Wallets Work?
To understand how Web3 wallets function, it’s essential to grasp the concepts of public and private keys, wallet addresses, and the transaction process within the blockchain framework.
Public and Private Keys
A Web3 wallet uses a pair of cryptographic keys: a public key and a private key. The public key is used to generate wallet addresses—similar to an account number—that others can use to send you funds. The private key, akin to a PIN or password, is kept secret and proves ownership of the assets in the wallet. It’s used to sign transactions, ensuring they can only be authorized by the wallet’s owner.
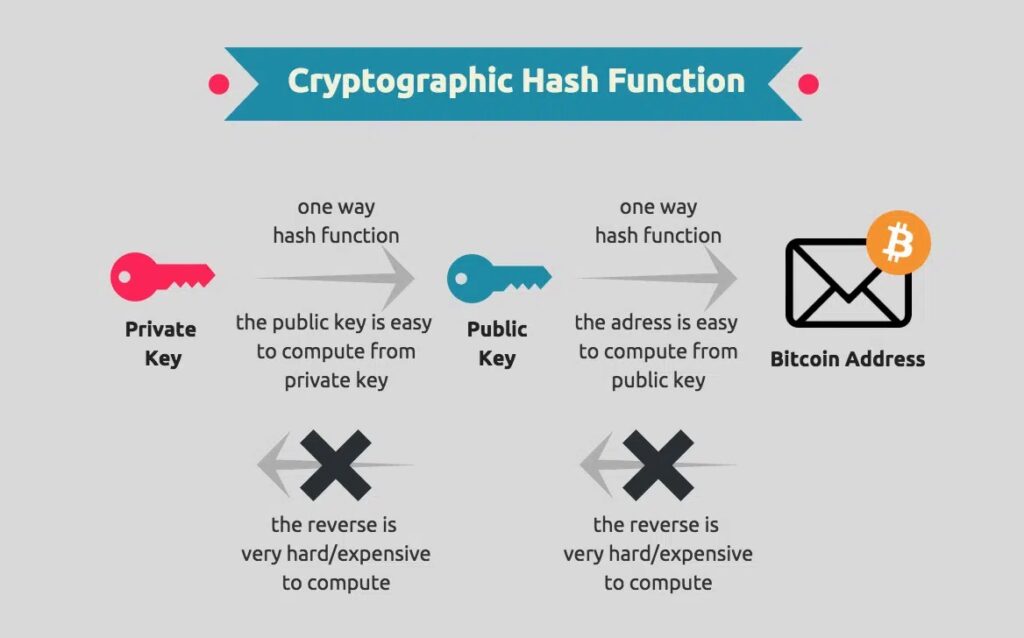
Wallet Addresses
A wallet address is derived from the public key and serves as the destination for receiving digital assets. It’s a string of alphanumeric characters that can be shared publicly. Each blockchain has a specific format for wallet addresses, and it’s crucial to use the correct address for the type of asset being sent to avoid loss of funds.
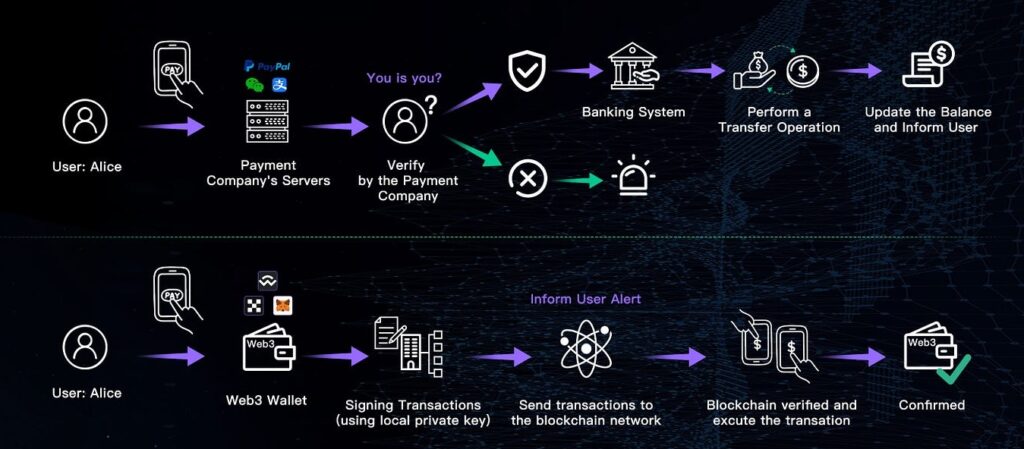
The Transaction Process
Executing a transaction with a Web3 wallet involves creating a transaction request, signing it with the private key, and broadcasting it to the blockchain network. Miners or validators then verify the transaction according to the network’s consensus rules. Once confirmed, the transaction is added to the blockchain, updating the distributed ledger and reflecting the transfer of assets.
Types of Web3 Wallets
Web3 wallets come in various forms, each with its own set of features, advantages, and use cases. Understanding the differences between hot wallets, cold wallets, and the platforms they operate on is key to choosing the right wallet for your needs.
Understanding Hot Wallets in Cryptocurrency
When it comes to the storage and management of cryptocurrencies, hot wallets are among the most accessible and dynamic options available for users. A hot wallet is essentially a digital wallet that is connected to the internet, and it is designed to offer quick and easy access to your crypto assets. This connectivity makes it incredibly convenient for regular trading and transactions, as they can usually be accessed through numerous devices such as smartphones, tablets, or computers.
Convenience vs. Security
Hot wallets are often recommended for the amount of crypto that you would carry in a physical wallet in your pocket—enough for day-to-day spending but not for your life savings. The reason for this is the inherent security risks that come with being online. Because they are connected to the internet, hot wallets are more susceptible to hacking, phishing scams, and malware than their offline counterparts, known as cold wallets or hardware wallets. A credible hot wallet provider will, however, implement various security measures such as two-factor authentication (2FA), encryption, and regular security audits to mitigate these risks.
Types of Hot Wallets
There are several different types of hot wallets, each with their own unique features:
1. Desktop Wallets: These are installed on your personal computer, providing a balance between accessibility and control over your assets. You have full control of your keys, but your security is as strong as your computer’s defenses.
2. Mobile Wallets: Installed on a smartphone, these wallets use QR code scanning for convenience and are ideal for daily transactions and payments on-the-go. They also utilize the phone’s security features, such as fingerprint recognition.
3. Web Wallets: As the most accessible type, these can be reached through any web browser. They do not require you to download or install anything but rely heavily on the wallet provider’s security measures.
4. Exchange Wallets: Many cryptocurrency exchanges offer built-in wallets for temporary storage while trading. However, the exchange controls the private keys to these wallets, which introduces a layer of risk.
The Importance of Private Keys
A crucial aspect to understand about hot wallets is the concept of private keys. These keys are what enable you to access and control your cryptocurrency. Hot wallets store these keys online, enabling you to sign off on transactions quickly. It is vital, however, to ensure that these private keys are kept secure, as anyone with access to them can potentially access your funds.
Best Practices for Hot Wallet Users
To bolster security when using a hot wallet, here are a few tips to follow:
- Always use strong, unique passwords for your hot wallet accounts.
- Enable two-factor authentication whenever possible.
- Keep the wallet’s software updated to the latest version.
- Be cautious of phishing websites and always access your wallet through official and secure channels.
- Only hold what you need for short-term use or trading in your hot wallet.
Hot wallets are invaluable for users who require regular access to digital assets as their online nature provides easy access and convenience for managing digital assets and interacting with dApps. While they offer user-friendly interfaces and quick transactions, their online nature makes them more vulnerable to hacking and phishing attacks. Users should weigh the benefits of convenience against the potential security risks. The low or no cost nature of hot wallet, when paired with their ease of use make them a great choice for those new to the web3 space.
Understanding the Security Advantages of Cold Wallets
Cold wallets, in contrast, are offline storage solutions for digital assets, offering enhanced security by minimizing exposure to online threats. Hardware wallets, a popular type of cold wallet, store private keys on a physical device that can connect to a computer when needed for transactions. Cold wallets are ideal for long-term storage of significant amounts of digital assets. Because they are detached from the internet, these wallets provide a robust shield against a multitude of cyber vulnerabilities that hot wallets might encounter.
Hardware Wallets: The Bastion of Digital Asset Security
A standout within the cold wallet family is undoubtedly the hardware wallet. These devices offer a reinforced layer of security by encapsulating your private keys within a tangible, portable form — typically resembling a USB stick or a small specialized device. Here’s how they enhance security:
1. Physical Protection: With your private keys securely stored on a hardware wallet, they never leave the device. This means that even when the hardware wallet is used on a potentially compromised computer, the keys themselves remain out of reach from malware or keyloggers.
2. Pin Codes and Backups: To amplify security further, hardware wallets often require a pin code to access the funds. Should the device become lost or damaged, users are usually provided with a recovery phrase or backup seed — a series of words that allows for the safe recovery of stored assets on a new device.
3. Limited Attack Surface: The hardware wallet’s exposure to potential threats is drastically reduced due to its offline nature. Transactions are signed offline before being broadcast on the blockchain, ensuring a secure transaction process.
The Ideal Cold Wallet Use-Case: Long-Term Storage for Significant Holdings
Cold wallets lend themselves particularly well to long-term investors, often referenced as “HODLers” within the cryptocurrency community — a term that originated from a misspelling of “hold” but has now come to characterize the strategy of holding onto digital assets with the expectation of long-term gains. For substantial digital asset portfolios, maintaining a significant portion in a cold wallet is analogous to keeping a valuable collection in a high-security vault; it’s about peace of mind and ensuring that one’s digital wealth is insulated from the unpredictability and volatility of online environments.
On the downside, cold wallets are less convenient for quick, daily transactions when compared to hot wallets. Therefore, a common strategy for asset holders is to use a combination of both: cold wallets for the bulk of assets and hot wallets for a smaller, readily accessible portion for everyday use. Ultimately, in an era where digital security is paramount, opting for a cold wallet, such as a hardware wallet, represents a strategic choice for those serious about the safekeeping of their digital currencies.
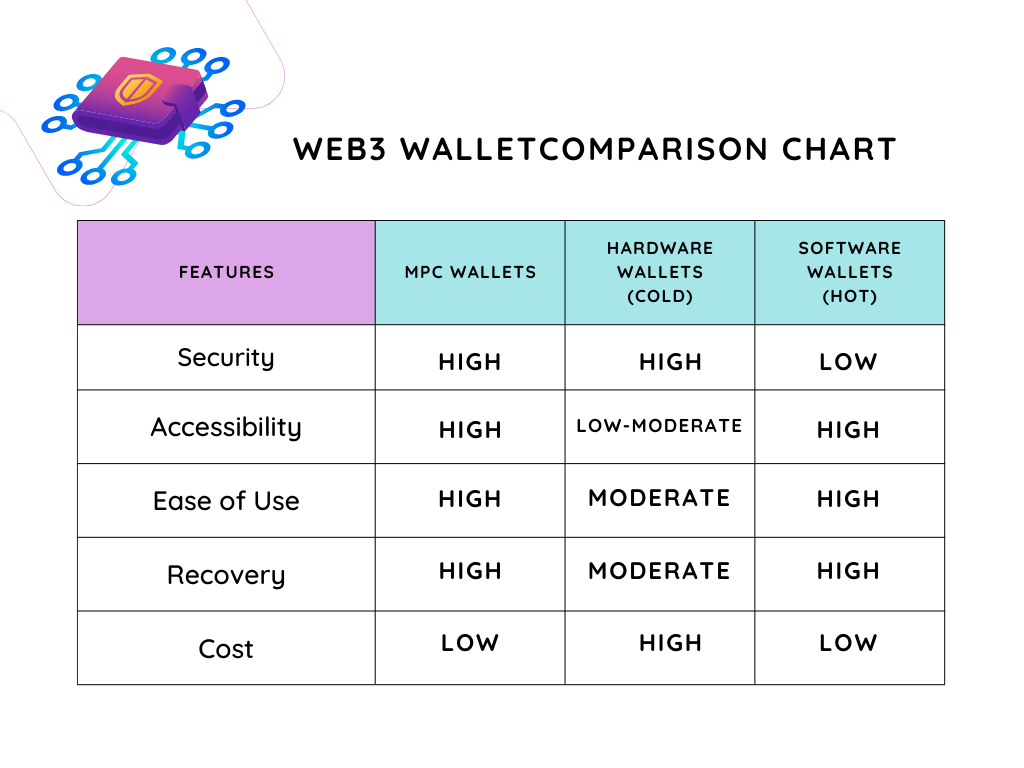
Multi-Party Computation Wallets (MPC)
A Multi-Party Computation (MPC) wallet is a type of cryptocurrency wallet that secures user funds and transactions through a cryptographic protocol involving multiple parties. Unlike traditional wallet models, which use single private keys for transaction signing, MPC wallets distribute the responsibility of signing a transaction across several parties. Each party holds a share of the signing key, and only by combining their parts can a transaction be authorized. This process enhances security by ensuring that no single party has control over the funds, significantly reducing the risk of theft or loss due to compromised keys.
Contrasting MPC wallets with hot and cold wallets highlights significant differences in security and accessibility. Hot wallets are connected to the internet, offering convenience and fast access for daily transactions but are more vulnerable to online attacks. Cold wallets, on the other hand, store assets offline, providing higher security at the expense of accessibility. MPC wallets offer a balanced approach by leveraging the security benefits of cold storage while maintaining some of the accessibility and flexibility of hot wallets. The distributed key management in MPC wallets minimizes the risks associated with single points of failure, as seen in traditional hot and cold wallet setups, making them a compelling option for both individual users and institutions looking for enhanced security without sacrificing functionality.
Enjoy our articles? You’ll love our newsletter!
Hashed Out is our bi-monthly newsletter introducing you to all things web3.
Choosing a Web3 Wallet
Selecting the right Web3 wallet requires considering several factors, including security features, user experience, compatibility with different blockchains, and the availability of backup and recovery options. As mentioned earlier, you can have more than one wallet and as you acquire more digital assets it would be recommended that you do.
Security Features
The security features of a Web3 wallet are paramount. Look for wallets with two-factor authentication (2FA), multi-signature support, and hardware wallet integration for added security layers. Understanding the security mechanisms in place can help safeguard your digital assets against unauthorized access and cyber threats.
User Experience
A wallet’s user experience can significantly impact your interaction with the digital economy. Opt for wallets with intuitive interfaces, clear transaction processes, and comprehensive support resources. A positive user experience can make navigating the complexities of Web3 more accessible and enjoyable, particularly when you are new to digital assets.
Compatibility
Compatibility with various blockchains and dApps is crucial for engaging with the broader Web3 ecosystem. Choose a wallet that supports the cryptocurrencies and blockchain platforms you’re most interested in, ensuring seamless transactions and interactions across different networks. As you can see from the ecosystem map below, some wallets support a specific blockchain, while others like Coinbase or MetaMask provide universal access.
Backup and Recovery Options
Reliable backup and recovery options are essential for recovering access to your wallet in case of device loss or failure. Most wallets provide recovery phrases— a series of words that can restore your wallet on a new device. Securely storing your recovery phrase is critical for safeguarding your assets against loss.

Web3 Wallet Features and Innovations
Web3 wallets continuously evolve, introducing new features and innovations to enhance functionality, security, and user experience. These advancements include multi-signature wallets, seamless dApp integration, DeFi accessibility, and NFT management.
Multi-Signature Wallets
Multi-signature (multi-sig) wallets require multiple parties to sign off on a transaction before it can be executed, adding an extra layer of security. This feature is particularly useful for organizations and teams managing shared funds, ensuring that no single individual has unilateral control over the wallet’s assets.
Integration With dApps
Modern Web3 wallets offer seamless integration with decentralized applications (dApps), enabling users to interact directly with DeFi platforms, games, and marketplaces. This integration simplifies the process of using dApps, making it easier for users to explore the decentralized web without leaving their wallet interface.
DeFi Accessibility
Web3 wallets play a critical role in accessing decentralized finance (DeFi) platforms, where users can lend, borrow, trade, and earn interest on their digital assets. Wallets that offer direct DeFi platform integration empower users to participate in the DeFi ecosystem, unlocking new opportunities for financial growth and investment.
NFT Management
With the rising popularity of non-fungible tokens (NFTs), Web3 wallets have adapted to provide comprehensive NFT management tools. Users can view, transfer, and interact with their NFTs directly from their wallets, facilitating engagement with digital art, collectibles, and virtual assets.
Best Practices for Web3 Wallet Security
Maintaining the security of your Web3 wallet is essential for protecting your digital assets. Adhering to best practices, such as keeping private keys secure, recognizing phishing attempts, and regularly updating software, can help minimize risks.
Keeping Private Keys Secure
The security of your Web3 wallet hinges on the confidentiality of your private keys. Never share your private keys or recovery phrases with anyone and avoid storing them online or in easily accessible locations. Using hardware wallets for key storage can significantly enhance security.
Recognizing Phishing Attempts
Phishing attacks are a common threat to Web3 wallet users. Be vigilant about unsolicited messages and emails requesting private information or urging you to click on suspicious links. Always verify the authenticity of websites and communications before interacting with them.
Regularly Updating Software
Keeping your wallet software and related applications up to date is crucial for security. Updates often include patches for vulnerabilities that could be exploited by attackers. Regularly updating your wallet ensures you benefit from the latest security features and enhancements.
The Future of Web3 Wallets
The future of Web3 wallets looks promising, with emerging trends, ongoing challenges with interoperability, and efforts to enhance user experience shaping the landscape.
Emerging Trends
Emerging trends in Web3 wallets include increased support for cross-chain transactions, integration of artificial intelligence for enhanced security, and the development of more user-friendly interfaces. These innovations aim to make Web3 wallets more versatile, secure, and accessible to a broader audience.
Interoperability Challenges and Solutions
Interoperability remains a significant challenge in the Web3 space, with efforts underway to enable seamless interaction among different blockchain networks. Wallets that support cross-chain functionality are at the forefront of addressing these challenges, facilitating transactions and asset management across diverse ecosystems. In the meantime, have a more universal wallet as part of your strategy can significantly mitigate this hassle.
Enhancing User Experience
Improving the user experience of Web3 wallets is a continuous focus for developers. Simplifying the onboarding process, offering educational resources, and integrating user feedback are key strategies for making Web3 wallets more approachable and enjoyable for users. As the use of wallets becomes more widespread the number of security and user experience enhancements wallets offer will surely expand as well.
Final Thoughts
Web3 wallets are the cornerstone for decentralized web usability, empowering users with control over their digital assets and providing a gateway to the vast possibilities of the blockchain. By understanding the various types of wallets, how they work, and the best practices for security, users can confidently navigate the Web3 space. As technology evolves, Web3 wallets will continue to play a vital role in the digital empowerment of individuals, offering a more inclusive, secure, and decentralized future of finance.
Ready to learn more about how a web3 strategy can benefit you?
Schedule a Friendly Conversation
Just 20 minutes could change your business — Free and Easy
